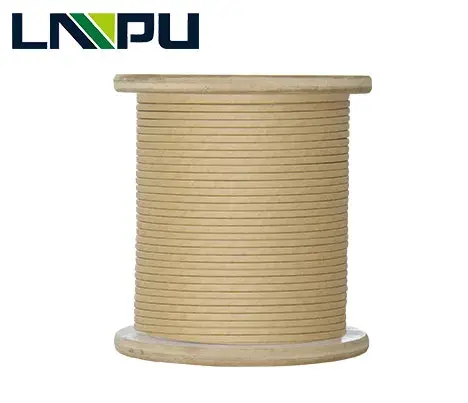
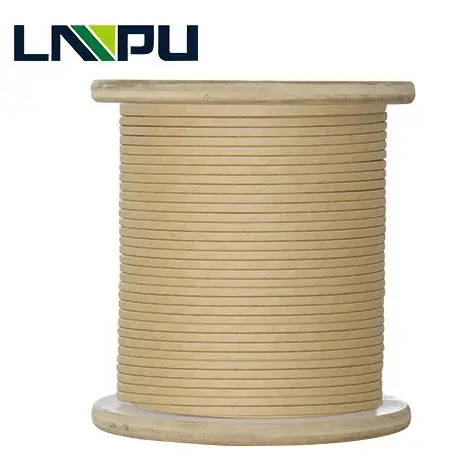
Special high thermal class paper covered wire – NOMEX wrapped wire
NOMEX wrapped paper enameled wire is a enameled wire extruded from an oxygen-free copper rod or an electrical round aluminum rod through a mold of a certain specification, and then wrapped by a T410 type NOMEX insulating paper. It is mainly used for transformers, electric welding machines, electromagnets Or other similar electrical equipment product windings.
Due to its high electrical, chemical and mechanical integrity, elasticity, flexibility, tear resistance, moisture and moisture resistance, NOMEX paper is very corrosive and will not be destroyed by insects, molds and fungi, it can be combined with All types of varnishes, adhesives, transformer fluids, lubricants, and refrigerants are compatible. In addition, NOMEX paper has a high heat resistance temperature. Even if the temperature is as high as 220 °C, it still maintains the original insulation performance. Transformers using NOMEX paper-covered wires can be used for Customers bring many economic, environmental and safety benefits.
Paper Covered Enameled Wire Manufacturing Process
Materials and Preparation
- Conductor Material:
- High-quality copper or aluminum wire is used as the conductor material. Copper is more commonly used due to its superior electrical conductivity.
- Insulating Materials:
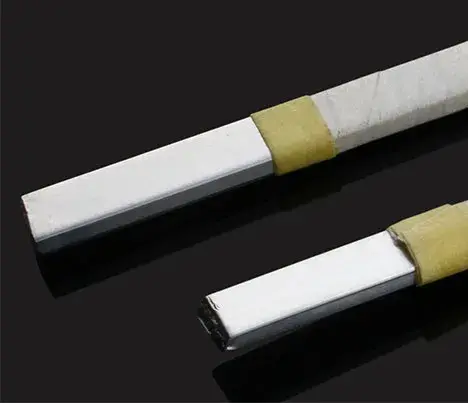
- Enameled wire: The wire is initially coated with an enamel insulating layer.
- Paper: Specially designed insulating paper is used to cover the enameled wire.
Manufacturing Process
1. Enameling
- Wire Drawing:
- The copper or aluminum wire is drawn to the required diameter using wire drawing machines.
- Cleaning:
- The wire is cleaned to remove any oxides, grease, or other contaminants that could affect the adhesion of the enamel.
- Annealing:
- The wire is annealed (heated and cooled) to relieve internal stresses and improve its flexibility and ductility.
- Enamel Coating:
- The clean and annealed wire is passed through an enamel application process where it is coated with a thin layer of insulating enamel.
- The coated wire is then passed through a curing oven where the enamel is baked onto the wire, forming a hard and durable insulating layer.
- Multiple layers of enamel may be applied, with each layer being cured before the next is applied, to achieve the desired insulation thickness.
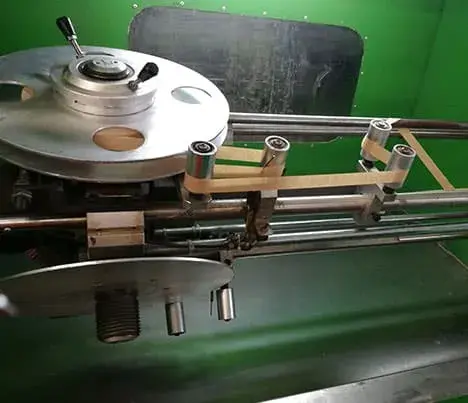
2. Paper Covering
- Paper Application:
- The enameled wire is then fed into a paper covering machine.
- Strips of insulating paper are precisely wrapped around the enameled wire. The paper can be applied in a single layer or multiple layers depending on the required insulation thickness.
- Taping and Binding:
- The paper is applied in a helical or longitudinal fashion, ensuring complete coverage of the enameled wire.
- The ends of the paper wrapping are typically secured using a small amount of adhesive or by tightly binding the paper to ensure it does not unravel.
3. Final Processing
- Drying and Curing:
- The paper-covered enameled wire may undergo a drying process to remove any moisture that could be present in the paper. This is crucial to maintain the insulating properties of the paper.
- The drying process usually involves passing the wire through an oven at a controlled temperature.
- Testing and Quality Control:
- The finished wire is subjected to a series of tests to ensure it meets all electrical, mechanical, and thermal specifications.
- Tests include measuring the insulation resistance, dielectric strength, and verifying the uniformity and integrity of the paper covering.
- Spooling and Packaging:
- The completed wire is carefully wound onto spools or reels, taking care to avoid any damage to the insulation.
- The spooled wire is then packaged appropriately to prevent damage during transportation and storage.
Quality Assurance
- Visual Inspection:
- Inspecting for any visible defects in the enamel and paper layers, such as cracks, bubbles, or gaps in coverage.
- Electrical Testing:
- Conducting tests to ensure the wire meets specified electrical properties, such as insulation resistance and dielectric breakdown voltage.
- Mechanical Testing:
- Verifying the mechanical properties of the wire, such as tensile strength and flexibility.
- Dimensional Checks:
- Ensuring the wire diameter and insulation thickness meet the specified tolerances.